TableLayout
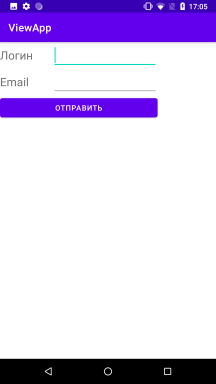
Контейнер TableLayout структурує елементи керування у вигляді таблиці за стовпчиками та рядками. Визначимо у файлі activity_main.xml елемент TableLayout, який міститиме два рядки і два стовпці:
<TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<TableRow>
<TextView
android:layout_weight="0.5"
android:text="Логин"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<EditText
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
</TableRow>
<TableRow>
<TextView
android:layout_weight="0.5"
android:text="Email"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<EditText
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
</TableRow>
</TableLayout>

Використовуючи елемент TableRow, ми створюємо окремий рядок. Як розмітка дізнається скільки стовпців треба створити? Android знаходить рядок із максимальною кількістю віджетів одного рівня, і ця кількість означатиме кількість стовпців. Наприклад, у цьому випадку в нас визначено два рядки і в кожному по два елементи. Якби в якомусь із них було б три віджети, то відповідно стовпців було б також три, навіть якщо в іншому рядку залишилося б два віджети.
Причому елемент TableRow успадковується від класу LinearLayout, тому ми можемо до нього застосовувати той самий функціонал, що й до LinearLayout. Зокрема, для визначення простору для елементів у рядку використовується атрибут android:layout_weight.
Якщо якийсь елемент має бути розтягнутий на низку стовпців, то ми можемо розтягнути його за допомогою атрибута layout_span, який вказує, на яку кількість стовпців треба розтягнути елемент:
<TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<TableRow>
<TextView
android:textSize="22sp"
android:text="Логин"
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<EditText
android:textSize="22sp"
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
</TableRow>
<TableRow>
<TextView
android:textSize="22sp"
android:text="Email"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<EditText
android:textSize="22sp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
</TableRow>
<TableRow>
<Button
android:text="Отправить"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_span="2"/>
</TableRow>
</TableLayout>
 Також можна розтягнути елемент на весь рядок, встановивши в нього атрибут
Також можна розтягнути елемент на весь рядок, встановивши в нього атрибут android:layout_weight=«1»:
<TableRow>
<Button
android:text="Отправить"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1" />
</TableRow>
Програмне створення TableLayout
Створимо TableLayout програмним чином, переклавши на код java найперший приклад із цієї статті:
package com.example.viewapp;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.TableLayout;
import android.widget.TableRow;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
TableLayout tableLayout = new TableLayout( this);
// перший рядок
TableRow tableRow1 = new TableRow(this);
TextView textView1 = new TextView(this);
textView1.setText("Логин");
tableRow1.addView(textView1, new TableRow.LayoutParams(
TableRow.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, TableRow.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, 0.5f));
EditText editText1 = new EditText(this);
tableRow1.addView(editText1, new TableRow.LayoutParams(
TableRow.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, TableRow.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, 1.0f));
// другий рядок
TableRow tableRow2 = new TableRow(this);
TextView textView2 = new TextView(this);
textView2.setText("Email");
tableRow2.addView(textView2, new TableRow.LayoutParams(
TableRow.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, TableRow.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, 0.5f));
EditText editText2 = new EditText(this);
tableRow2.addView(editText2, new TableRow.LayoutParams(
TableRow.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, TableRow.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, 1.f));
tableLayout.addView(tableRow1);
tableLayout.addView(tableRow2);
setContentView(tableLayout);
}
}
Приклад
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!-- Стовпець 1 буде автоматично розтягуватися -->
<TableLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:stretchColumns="1"
android:padding="16dp">
<!-- Заголовок таблиці -->
<!-- Об'єднання двох стовпців -->
<TableRow>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Дані клієнта"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:textStyle="bold"
android:layout_span="2"
android:gravity="center" />
</TableRow>
<!-- Рядок 1: Ім'я -->
<TableRow>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Ім'я:" />
<EditText
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="Введіть ім'я"
android:inputType="textPersonName" />
</TableRow>
<!-- Рядок 2: Телефон -->
<TableRow>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Телефон:" />
<EditText
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="Введіть телефон"
android:inputType="phone" />
</TableRow>
<!-- Рядок 3: Email -->
<TableRow>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Email:" />
<EditText
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="Введіть email"
android:inputType="textEmailAddress" />
</TableRow>
<!-- Рядок 4: Кнопки -->
<TableRow>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Очистити" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Зберегти" />
</TableRow>
</TableLayout>
Коли використовувати TableLayout
Ситуації для використання:
- Табличні форми: наприклад, для введення даних користувача чи форм замовлень, де кожен рядок містить мітку та відповідне поле для введення.
- Звіти: відображення невеликої кількості даних у табличному вигляді (наприклад, кількість замовлень чи статистика).
- Прості таблиці: коли потрібно забезпечити вирівнювання елементів за стовпцями.
RecyclerView: кращий вибір для великих табличних даних, оскільки підтримує оптимізовану роботу з великим набором елементів і додає можливості для прокручування.
